
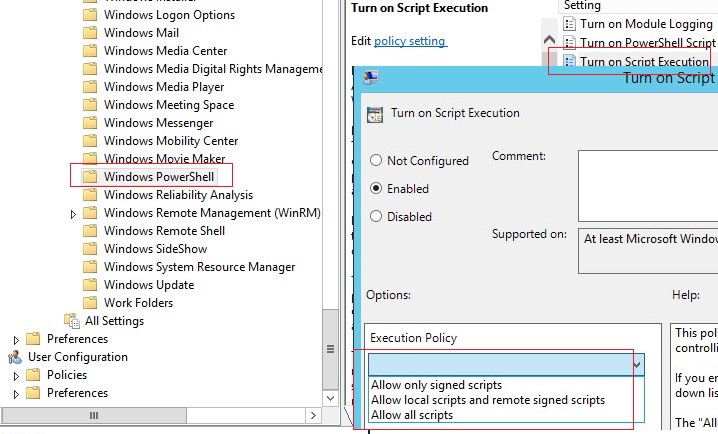
This allows you to split a large, long, and complex logon script into several small scripts and execute them quickly and easily. The scripts can also be quickly and easily integrated into Group Policy without any big changes. In many cases, the AD user account settings are used for this purpose. One example of centralized script usage is to assign Active Directory (AD) users logon scripts that a computer executes when the employee logs on. In this article, I will show you how to make life easier with Windows scripts. Microsoft offers various options for integrating scripts into Group Policy, which makes the administration of computers extremely flexible. These scripts start automatically when you log on or log off and when you boot up or shut down the computer.

I am unable to change the logon script to run the unmap command first - they are inaccessible to me because of security measures.Various kinds of scripts are available for automating tasks in Windows. As long as I run the unmap command before a reboot it's fine for the next boot. But a reboot after that back to slow logon script and drives that won't connect. If I run an UNmap command "net use * /d /y" which takes about 15 minutes to complete and I reboot it runs the logon script fine on the next boot and drives connect OK. Even clicking on them in Explorer starts a progress bar and it never connects. I found that logon scripts now take 15 minutes to complete and when they do drives mapped to a Windows 2003 server will not connect. SMB1 is installed due to an older server we have issues with to upgrade. Was running Windows 1909 all drive mappings worked fine. Started experimenting on a few test PCs at work, running Windows 10 Enterprise on a corporate LAN. I put it on 4 PCs at home, no major issues. Been fooling with Windows 10 20.04 update.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
